
With the popularity of service oriented architectures, inter service communication technologies like SOAP and REST became heavily used in the softwate industry. Initially it was SOAP, and then REST style HTTP APIs became widely popular. As time went on engineers in Facebook thought of creating a new technology to communicate with the backend APIs which mitigated the specific problems they faced while using REST and other traditional style APIs. That was the origin of GraphQL.
GraphQL is defined as a query language for APIs. It allows the API consumer to specify which data they need specifically in JSON format and the GraphQL runtime returns just that data. In the server side, a runtime handles the consumer requests and manages handling of data.
For example, a front end service could send the below request to the GraphQL backend.
{
hero {
name
}
}
And it will return the following
{
"hero": {
"name": "Paul Atreides"
}
}
Here, only the specific data field is returned to the user, without defining any specific DTOs or cluttered responses.
GraphQL Schema
Same as SOAP WSDLs, a GraphQL service has a service definition, a file with the extension graphql which defines the types and queries of the GraphQL service. Typically, a backend library takes this schema as an input and generates service stubs needed. The developer could then implement the specific stubs and code their implementation. A GraphQL schema consists of various components such as
- Queries
- Type
- Mutations
The most important of these types are Query and Type. A type defines a data-structure which is used to encapsulate data.
type Hero {
id: ID
name: String
age: Int
movie: String
}
A Query defines the set of queries an API consumer can invoke, Example below.
type Query {
heroById(id: ID) : Hero
heroByMovie(movie: String) : Hero
}
You can read more about these by refereing the GraphQL documentation.
Spring GraphQL
As the most popular Java framework for creating backend services, Spring also provides powerful libraries to create GraphQL services.
Creating the project
The easiest way to create a Spring project is using the Spring Initializer. Navigate to the Spring Initilizer and use the following configuration and generate a new project, open it with your favorite browser.
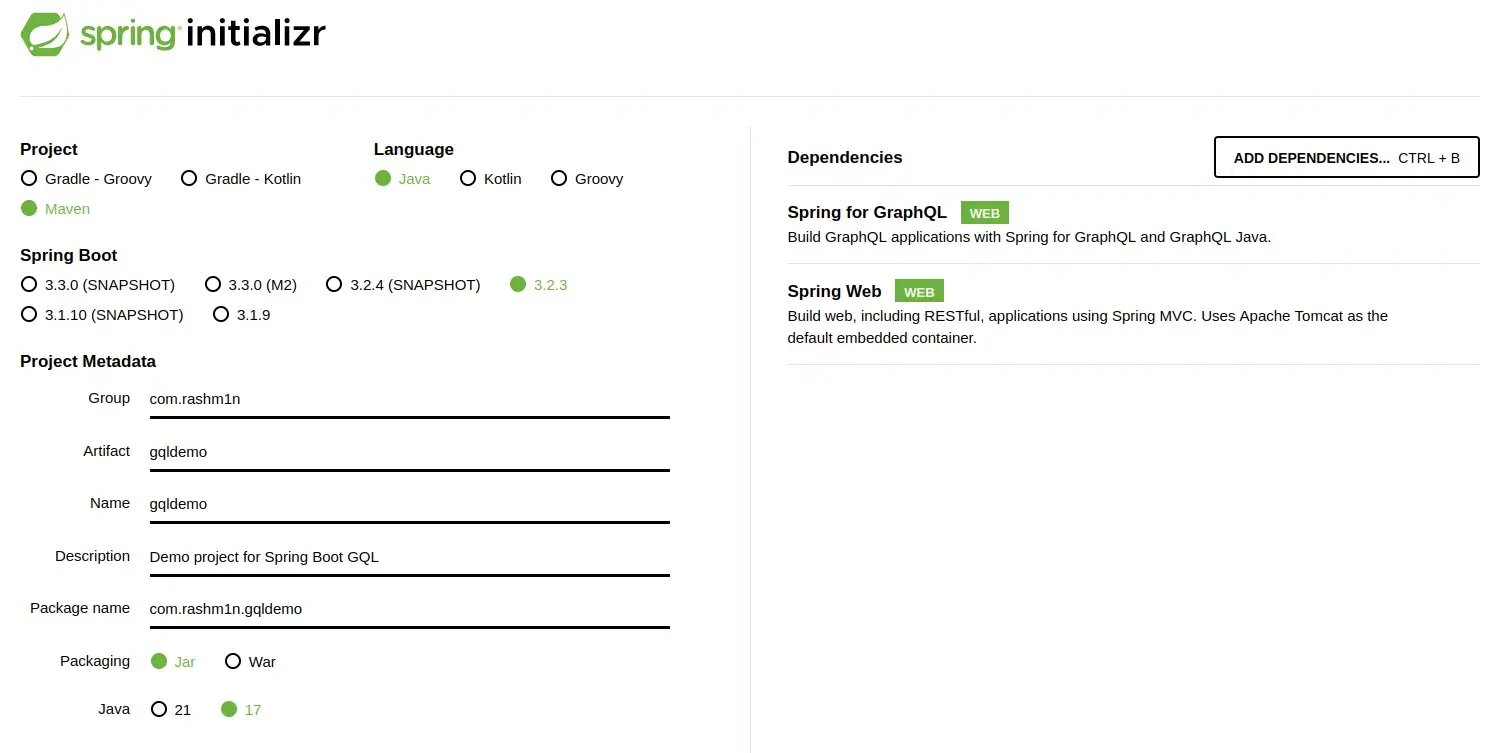
Inside the created folder structure, you can see a folder named graphql inside the resources directory. This is the location where your GraphQL schema should reside. A simple GraphQL schema is given below.
type Query {
heroById(id: ID) : Hero
}
type Hero {
id: ID
name: String
age: Int
movie: String
}
Save this schema as schema.graphql and put it inside the resources/graphql folder.
Implementation
Now we should create the types defined in the schema. In our simple schema, we have a single type Hero. We can create this inside the src directory.
package com.rashm1n.gqldemo;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public record Hero (String id, String name, int age, String movie) {
private static List<Hero> heroes = Arrays.asList(
new Hero("hero-1", "Paul Atreides", 16, "Dune"),
new Hero("hero-2", "Duncan Idaho", 40, "Dune"),
new Hero("hero-3", "Chani", 16, "Dune 2")
);
public static Hero getById(String id) {
return heroes.stream()
.filter(hero -> hero.id().equals(id))
.findFirst()
.orElse(null);
}
}
Then we need to map the defined queries in the schema, with the relevant data fetcher. We can do this via a Spring @Controller.
package com.rashm1n.gqldemo;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.Argument;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.QueryMapping;
import org.springframework.graphql.data.method.annotation.SchemaMapping;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class HeroController {
@QueryMapping
public Hero heroById(@Argument String id) {
return Hero.getById(id);
}
}
Now our simple GraphQL service is completed. Now we could run this code and execute some queries and see the results. Spring provides a built in GraphQL playground for easy query execution, so that the developer does not need additional tools to invoke the API. We could enable this by adding the following property to the application.properties file inside the resources directory.
spring.graphql.graphiql.enabled=true
spring.graphql.graphiql.path="/graphiql"
After this, start your application.
mvn spring-boot:run
Testing
After the application is started, navigate to `http://localhost:8080/graphiql” . A GraphQL UI playground like below would appear.
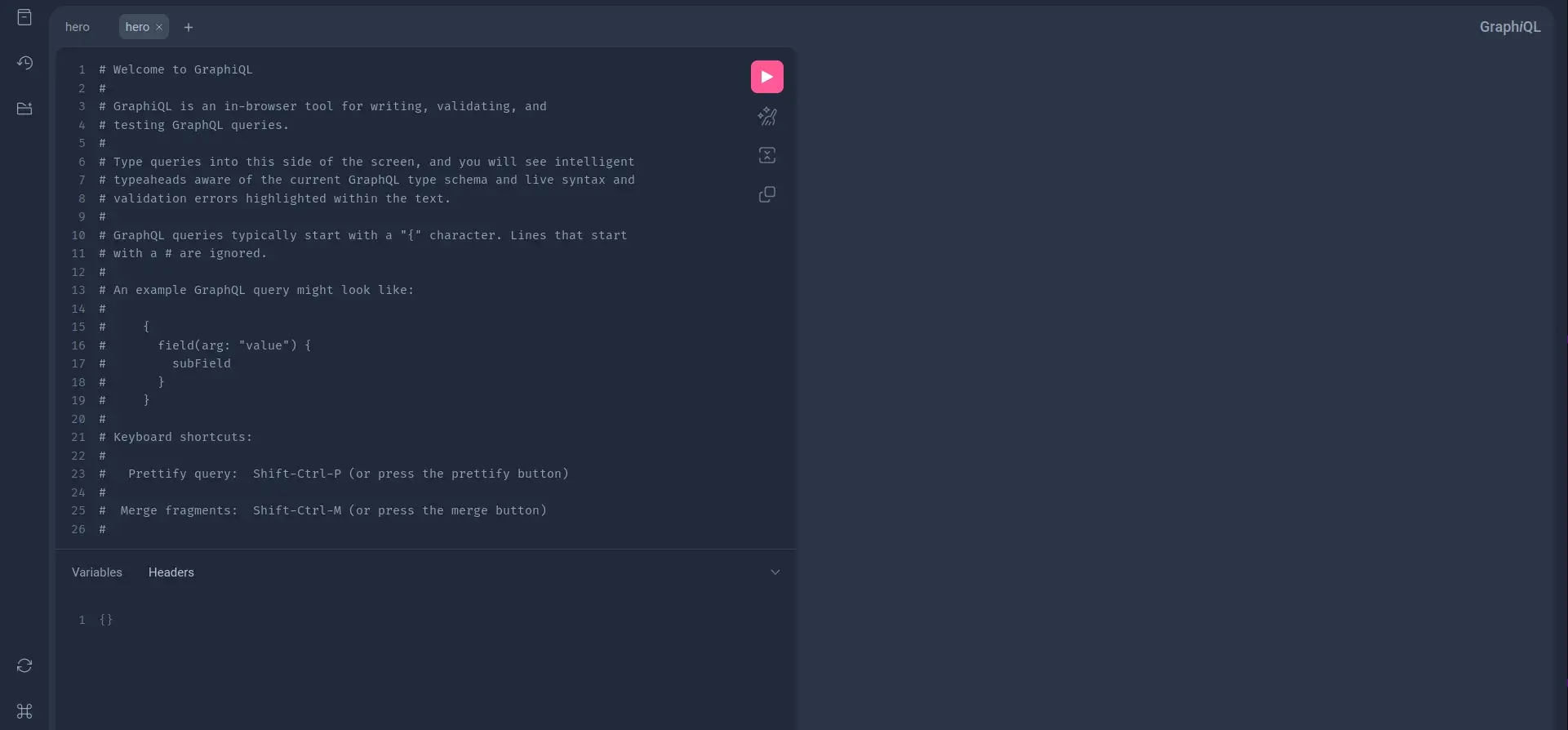
In the right side of the console, you could enter a query and run via clicking the run button. The result will appear in the right side. Let’s enter the following query and see what the output is.
query hero {
heroById(id: "hero-1") {
id
name
}
}
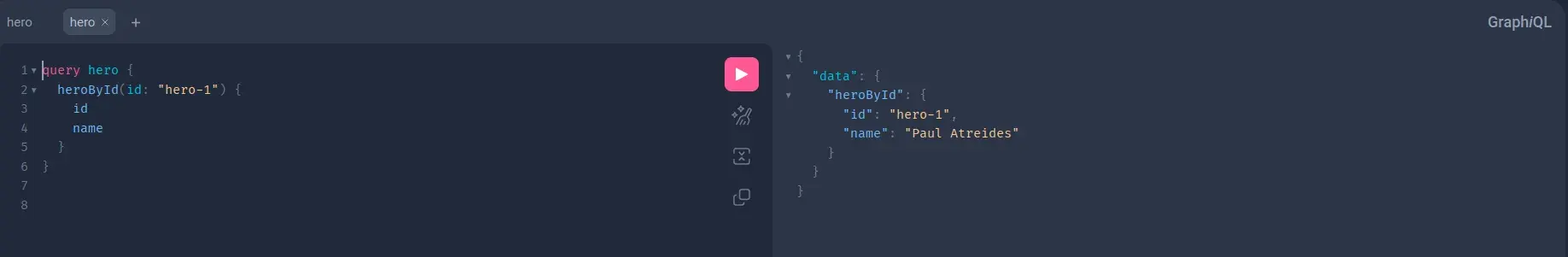
As you can see, the correct entry is included in the response. And furthermore, ONLY the fields we explicitly requested are returned, other fields are excluded from the response.
You can add more queries and types and play around a bit using this console to get a better idea :)
This has been a short introduction to GraphQL and using GraphQL with Spring Boot. Hope you enjoyed the article !
Find the below links for more details about GraphQL and Spring GraphQL.